Introduction
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is revolutionizing the way businesses track and manage assets. At the heart of every RFID system lies the RFID reader—a crucial component that enables the exchange of data between tags and business systems. But what exactly is an RFID reader, how does it work, and why is it important across industries? In this blog, we’ll explore the fundamentals of RFID readers, their components, different types, and how they are transforming asset tracking in modern operations.
What is an RFID Reader?
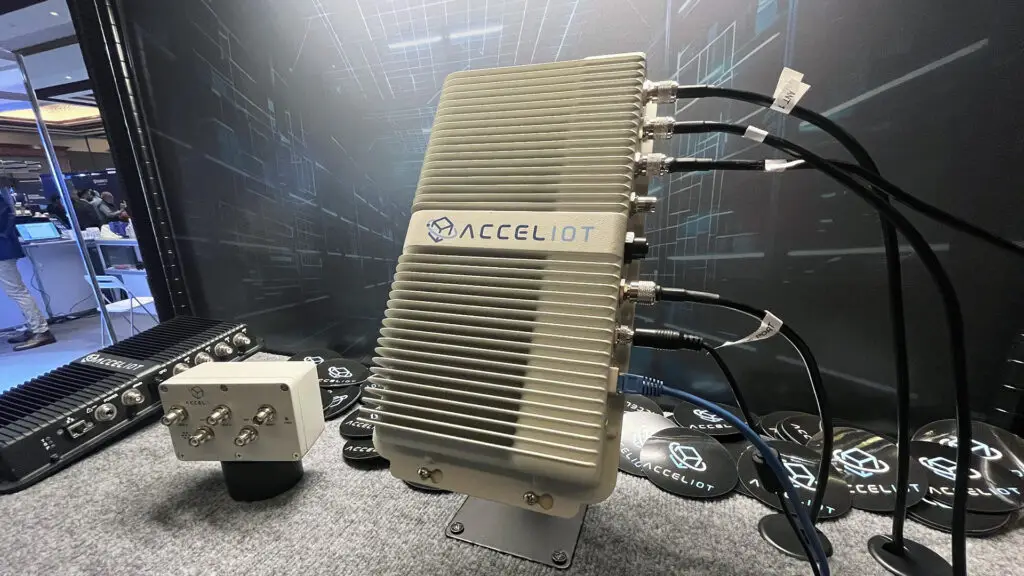

An RFID reader is a device that is used to capture information from RFID tags. It reads the data encoded in RFID tags and transfers it to a computer system for processing. Unlike barcode scanners, which require line-of-sight to read information, RFID readers can collect data wirelessly from tags within a certain range, even if the tags are not directly visible. This makes RFID readers a powerful tool for tracking and managing assets in real-time.
RFID readers can be either fixed or handheld, depending on the specific application. They are a key part of the broader RFID system, which also includes tags, antennas, and software to ensure efficient asset tracking and management.
How Does an RFID Reader Work?
RFID readers operate by emitting radio waves that power up RFID tags within their range. When a tag is activated, it sends back its data to the reader, which then communicates this information to the central database or software for further analysis.
The RFID reader works alongside RFID antennas, which amplify the signal and help identify the exact location of the tag. Depending on the type of reader—fixed or handheld—the strength and range of these signals can vary, making RFID systems versatile for use across different environments.
Key Components of an RFID Reader
An RFID reader is part of a more extensive system that includes several important components, all working together to ensure seamless data capture.
RFID Tags: How They Interact with Readers

RFID tags contain data about the item to which they are attached. When an RFID reader emits radio waves, it powers up the RFID tag, which then transmits its stored information back to the reader. This data can include anything from a product’s serial number to specific asset information, allowing for detailed tracking.
RFID antennas play a significant role in expanding the reader’s coverage area. They transmit and receive signals between the RFID tags and the reader, ensuring that tags are read accurately even in complex environments. Antennas are crucial in optimizing the efficiency of the RFID reader and ensuring consistent communication.
RFID Software: Enabling Real-Time Tracking
RFID software is responsible for processing the data collected by the RFID reader. It helps store, analyze, and integrate the data into existing business systems, providing real-time tracking of assets and enabling informed decision-making. This software is key to transforming raw RFID data into actionable insights that drive business success.
Types of RFID Readers: Fixed vs. Handheld
RFID readers come in two primary types: fixed and handheld. Both types have distinct features and are suited to different applications based on operational requirements.
Benefits of Fixed RFID Readers for Asset Visibility
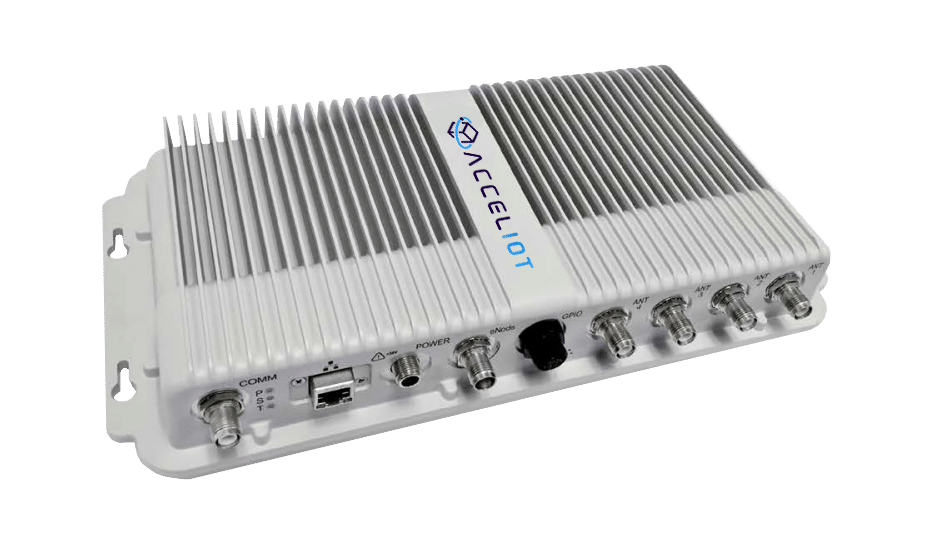

Fixed RFID readers are typically mounted at key locations, such as entry/exit points or along conveyor belts. They are ideal for environments where continuous, automated tracking is required, such as in warehouses and manufacturing facilities.
- Automated Tracking: Fixed readers automate the tracking process, allowing for seamless scanning of multiple tags without manual intervention.
- High Throughput: They are capable of reading thousands of tags in a short time, making them perfect for high-volume environments.
- Reduced Labor Costs: With fixed readers, companies can minimize the need for manual inventory checks, saving time and reducing labor costs.
Advantages of Handheld RFID Readers for Mobility
Handheld RFID readers provide flexibility and mobility, allowing workers to move freely while scanning items. They are often used in applications where manual verification is needed or where assets are spread over a large area.
- Portability: Handheld readers are portable, making them suitable for environments where flexibility is key, such as retail stores or field service operations.
- On-Demand Scanning: These readers allow for targeted scanning, which is useful for spot-checks, inventory audits, or locating specific items within a facility.
- Versatility: Handheld readers can be used across different areas, providing on-demand asset visibility without the need for a fixed infrastructure.
Applications of RFID Readers Across Industries
RFID readers are used in various industries to enhance operational efficiency and visibility.

In warehousing, RFID readers are used to automate inventory tracking and reduce manual labor. Fixed readers at key points within the warehouse can continuously track inventory movement, ensuring real-time visibility of stock levels and minimizing human error.
In supply chain management, RFID readers provide visibility across all stages of product movement. By using a combination of fixed and handheld readers, companies can monitor goods in transit, verify shipments, and ensure that inventory is accurately accounted for, from production to delivery.
In healthcare facilities, RFID readers help track medical equipment, manage patient records, and ensure medications are correctly administered. This improves patient safety and reduces time spent locating essential items.
In retail, RFID readers improve inventory accuracy, support anti-theft measures, and provide a better shopping experience. Handheld readers are often used for inventory audits, while fixed readers help track stock levels in real time.
RFID Reader vs. Barcode Scanner: Which is Better?
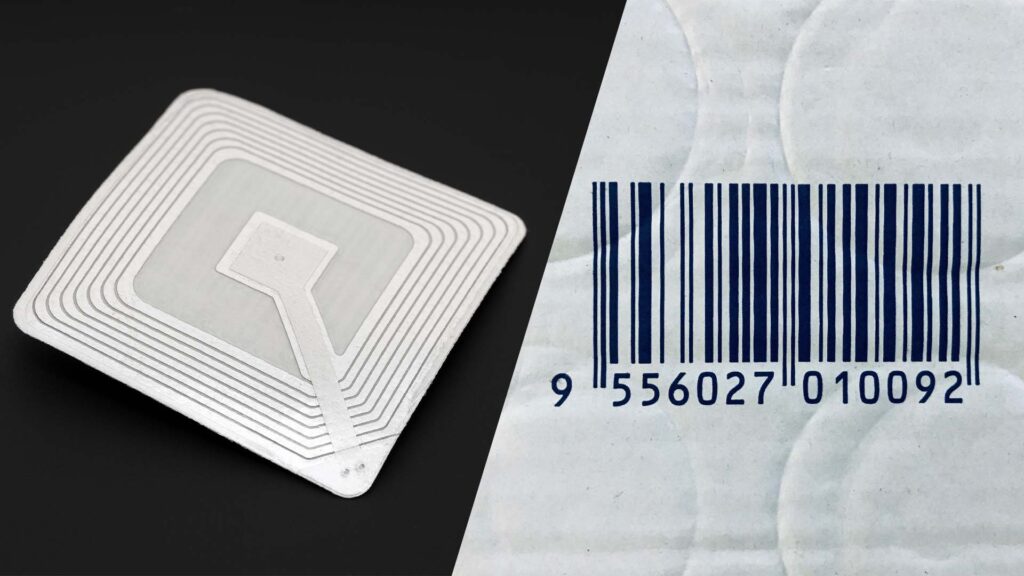

Both RFID readers and barcode scanners are used for tracking assets, but there are significant differences between the two. RFID readers can read multiple tags at once, without the need for direct line-of-sight, making them much more efficient in high-volume scenarios. Barcode scanners, on the other hand, require a clear line of sight and can only scan one item at a time, which can slow down processes in larger operations.
RFID readers also have the advantage of reading tags from a distance, while barcode scanners need to be in close proximity. While barcode scanners are generally more affordable, the efficiency and accuracy provided by RFID readers make them a superior choice for businesses looking to optimize their asset tracking and inventory management processes.
Benefits of RFID Readers in Modern Asset Tracking
RFID readers offer several benefits that make them an integral part of modern asset tracking systems.
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
RFID readers eliminate the need for manual data entry, reducing errors and improving the accuracy of inventory and asset records. The ability to read multiple tags simultaneously means that inventory counts can be completed much faster compared to traditional methods.
Real-Time Visibility of Assets
RFID readers provide real-time data on the location and movement of assets, allowing businesses to react quickly to changes in demand or to locate missing items. This visibility is crucial for maintaining efficient operations and ensuring that assets are where they need to be.
Cost Savings and Scalability
By automating asset tracking and reducing manual processes, RFID readers help lower labor costs and increase productivity. Additionally, RFID systems are highly scalable, making it easy for businesses to expand their asset tracking capabilities as they grow.
The Future of RFID Readers and Technology Innovations
The future of RFID readers looks promising, with ongoing innovations that aim to enhance their capabilities and make them more accessible to businesses of all sizes. Integration with IoT (Internet of Things) is one of the key trends, allowing RFID readers to work seamlessly with other connected devices to provide even greater visibility and control over assets.
Advancements in antenna design are also improving the range and accuracy of RFID readers, making them suitable for even more challenging environments. As the cost of RFID technology continues to decrease, we can expect to see more widespread adoption across industries, leading to more efficient, connected, and automated operations.
Conclusion
RFID readers are an essential part of modern asset tracking and management systems, offering significant advantages in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and real-time visibility. Whether used in warehousing, healthcare, retail, or supply chain management, RFID readers are transforming the way businesses operate and helping them stay competitive in a rapidly changing world.
Ready to explore how RFID readers can benefit your business? Contact Acceliot today for a free consultation and demo of our advanced RFID solutions. Let us help you optimize your asset tracking and improve operational efficiency with our state-of-the-art technology.