Introduction
In an increasingly connected world, the need to efficiently track and manage assets has never been more crucial. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is at the forefront of this transformation, providing a powerful way for industries to improve efficiency, accuracy, and visibility in their operations. But what is RFID, how does it work, and why is it being hailed as a game-changer across numerous sectors? In this blog, we’ll dive into what RFID is, how it functions, its core components, and why it’s such a revolutionary tool in modern industries.
What is RFID (Radio Frequency Identification)?
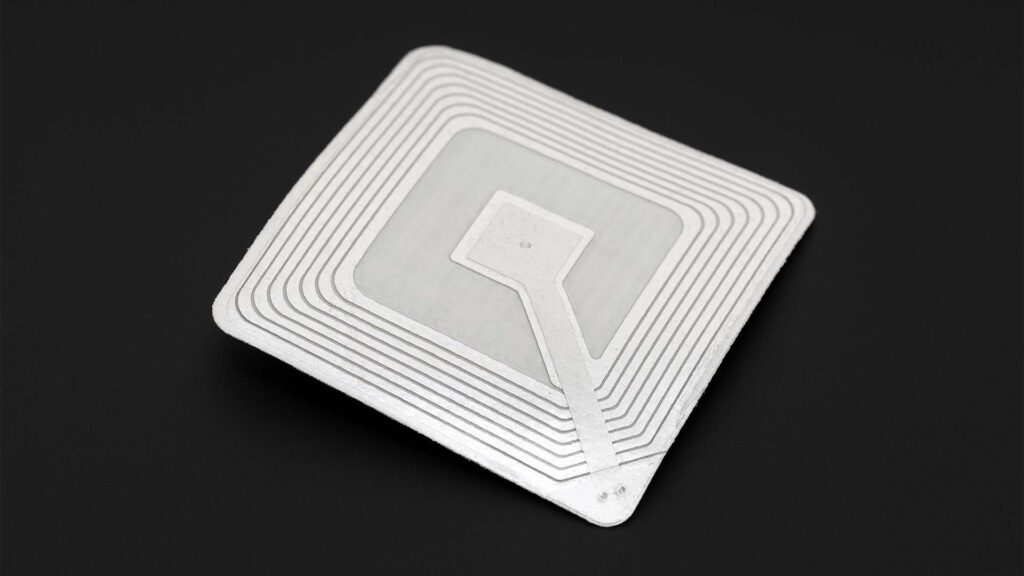

RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information, which can be read by specialized devices called RFID readers. Unlike barcodes, which require line-of-sight, RFID technology allows for non-contact, non-line-of-sight identification, making it a versatile and efficient tool for tracking and managing assets across various industries.
RFID technology is used in a wide range of applications, from tracking products in a warehouse to managing patient information in healthcare facilities. Its ability to provide real-time data and automate processes makes it an invaluable tool for boosting productivity and accuracy in operations.
How Does RFID Work?
At its core, RFID technology operates using radio waves to communicate between a tag and a reader. Here’s a simplified look at how it works:
- RFID Tags are attached to items that need to be tracked. These tags contain a microchip that stores information about the item.
- RFID Readers emit radio waves that power the tag and extract the information stored on it.
- The data is then processed and analyzed by RFID software, which helps organizations make informed decisions based on real-time insights.
RFID technology can be used at different frequencies, each with its unique characteristics and suitable applications. The ability to read multiple tags simultaneously and from a distance gives RFID a significant advantage over traditional tracking technologies.
The Core Components of an RFID System
An RFID system is composed of several essential components that work together to deliver seamless asset tracking. These include tags, readers, antennas, and software.
RFID Tags: Types and Uses

RFID tags are the identifiers that are attached to objects. They store data about the object, which can be read by an RFID reader. There are two main types of RFID tags: Active and Passive.
- Active RFID Tags: These tags have their own power source and can transmit signals over longer distances. They are often used in applications where a large range is required, such as vehicle tracking.
- Passive RFID Tags: (Depicted above) These tags do not have an internal power source and are powered by the reader’s signal. They are less expensive and are used in applications like inventory tracking and access control.
An RFID reader is a device that communicates with RFID tags to obtain the data stored on them. RFID readers come in different forms, including handheld and fixed readers, depending on the use case.
- Handheld Readers are portable and are used for flexibility in tracking items in warehouses or retail environments.
- Fixed Readers are mounted at specific points, such as entrances or conveyor belts, for automated reading of tags.
When choosing an RFID reader, consider the range required, the environment it will be used in, and the type of tags that need to be read.
RFID Antennas: Types and Functions
RFID antennas are a crucial part of the system, as they are responsible for transmitting and receiving radio waves between the tags and the reader. Antennas can vary based on their design, frequency range, and intended use.
- Linear Polarized Antennas: Best for applications where tags are consistently aligned.
- Circular Polarized Antennas: Ideal for environments where tag orientation is variable, providing more consistent reads.
RFID Software: Enabling Integration and Insights
RFID software acts as the brain of the system. It processes data collected from RFID tags and readers, integrates it into existing business systems, and provides actionable insights.
RFID software helps manage data, generate reports, and improve decision-making. Its ability to integrate with other enterprise systems, such as warehouse management or inventory software, makes it an essential component of an efficient RFID solution.
The Types of RFID Systems and Frequencies
RFID systems operate at different frequencies, each with unique capabilities and suitable applications.
Active vs. Passive RFID: What’s the Difference?
- Active RFID: Uses a battery-powered tag to broadcast signals to a reader. These tags are ideal for tracking high-value assets over long distances.
- Passive RFID: Relies on the reader’s energy to power the tag. This type is more affordable and commonly used for applications like inventory tracking.
Low, High, and Ultra-High Frequencies Explained
- Low Frequency (LF): Operates at 125-134 kHz. Used for short-range applications, such as animal tracking and access control.
- High Frequency (HF): Operates at 13.56 MHz. Typically used in ticketing, payment, and library systems.
- Ultra-High Frequency (UHF): Operates between 300 MHz and 3 GHz. It is ideal for long-range applications, such as warehouse inventory management.
Applications and Use Cases of RFID
RFID technology is used in a variety of industries to enhance operational efficiency and visibility.

In warehousing, RFID helps automate inventory tracking, reducing manual labor and improving accuracy. It enables real-time visibility of stock levels, ensuring that companies always know what is available and where it is located.
In supply chain management, RFID provides end-to-end visibility, allowing stakeholders to monitor the movement of goods through each stage of the supply chain. This real-time information helps reduce delays, prevent theft, and ensure timely deliveries.
RFID is used to track medical equipment, manage patient information, and ensure that the right medications are administered. It helps in reducing human error, increasing efficiency in locating assets, and maintaining accurate records.
RFID improves inventory accuracy, prevents theft, and provides a better shopping experience by ensuring items are in stock. It also allows retailers to gain insights into consumer preferences and optimize stock levels based on real-time demand.
RFID is used to track servers, network equipment, and other critical assets. RFID enables real-time visibility into the location and status of each asset, helping data center managers streamline maintenance, prevent misplacement, and ensure optimal performance. By automating asset management, RFID reduces the need for manual checks, thereby minimizing downtime and operational costs.
RFID is used to track parts, components, and finished vehicles throughout the production process. RFID tags attached to parts enable manufacturers to monitor the location and status of each component in real time, ensuring that the right parts are available at the right time. This improves production efficiency and reduces the risk of delays. Additionally, RFID is used to manage vehicle inventory in large lots, making it easier to locate specific vehicles for quality checks, shipping, or further processing.
The Benefits of RFID Technology
RFID can deliver business value as part of a holistic automation and asset visibility initiative.
Improved Inventory Accuracy
RFID eliminates manual errors in inventory management by providing automatic and accurate item tracking. This leads to higher accuracy rates and reduced discrepancies in stock levels.
Reduced Operational Costs
By automating tasks such as inventory counts and asset tracking, RFID reduces the need for manual labor, leading to lower operational costs and increased productivity.
Real-Time Asset Visibility
RFID provides real-time data on the location and movement of assets, which is essential for businesses looking to improve their decision-making and respond quickly to changes in demand.
Challenges and Considerations for RFID Implementation
While RFID offers numerous benefits, there are challenges to consider.
Security and Privacy in RFID Systems
RFID systems can be susceptible to security risks, such as unauthorized access and data breaches. Ensuring proper encryption and data protection measures are in place is critical for mitigating these risks.
Cost Feasibility of RFID Solutions
The cost of RFID implementation can be significant, especially for smaller businesses. Evaluating the return on investment and assessing whether the benefits outweigh the initial costs is an important step before adoption.
RFID vs. Barcodes: Which is Better for Modern Tracking?
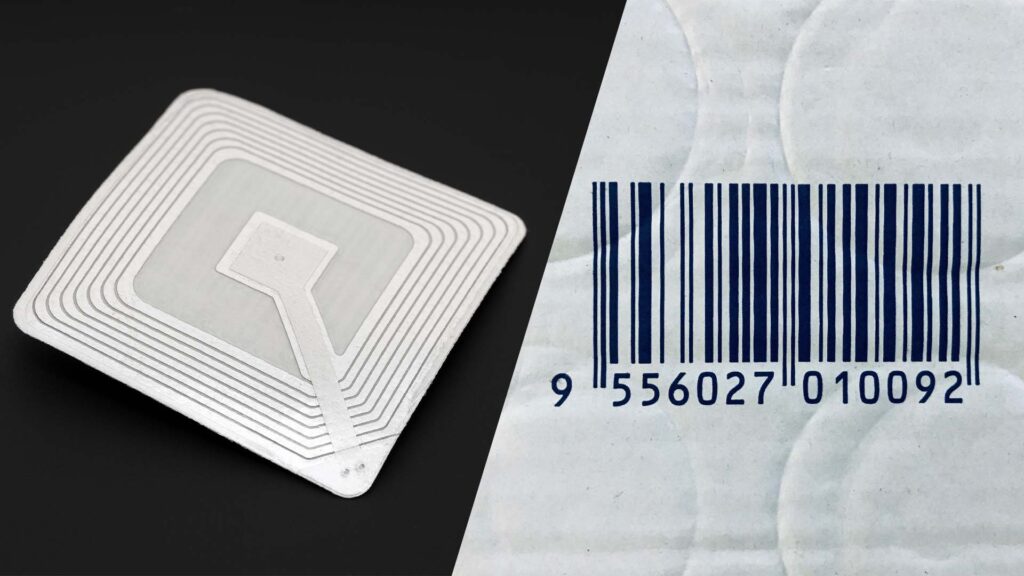

RFID and barcodes are both popular tracking technologies, but RFID offers several advantages over barcodes. Unlike barcodes, RFID tags do not require line-of-sight and can be read from a distance. This capability allows for faster scanning of multiple items at once, reducing the time and labor required for inventory management. However, barcodes are more cost-effective and may be preferable for smaller businesses or simple applications.
Ready to revolutionize your asset management? Contact Acceliot today for a demo or to discuss RFID solutions tailored to your industry.
